Colombia has now topped the list of foreign countries searching Miami real estate in nine of the last 10 months.
Posts
In what’s being billed as one of the biggest and most ambitious urban redevelopment schemes in the country, Miami-Dade County has packaged some 17 acres of publicly owned downtown real estate and put it up for bid.
Emilio Palomo (the past chair of the Master Brokers Forum, an elite network of the top real estate professionals in Miami, and the owner/broker of Riteway Properties III) recently went to a party for the opening of a Miami Beach hotel.
He was not familiar with this particular hotel or the people behind it, and attended on the invitation of a colleague. After a few minutes, it became clear to him that most of the guests were from Argentina (or of Argentine descent), and he was not surprised to learn that the owners are themselves native Argentines who have been — somewhat quietly — buying and upgrading Miami Beach hotels for many years.
Emilio worked with buyers and sellers from around the world over the course of his 47-plus years in Miami real estate. He feels fortunate to live in a city that draws so much global interest, with buyers coming from Europe, Asia, Latin America, Canada, and (of course) the U.S. Many find our real estate prices to still be reasonably low compared to their home nations.
Some foreign buyers come here because of political instability and lack of security in their countries, others because of our weather, beaches and everything else Miami has to offer. Whatever the reason, Miami has become one of the most desired international destinations in today’s market for a permanent or second (or third!) home.
And while buyers from Russia, Brazil, Colombia and Venezuela have drawn the biggest headlines for their respective impacts, he believes that Miami’s Argentines have not received nearly enough attention for their significant contribution to the economy and real estate market.
Some of this may be due to the nature of Argentines themselves, who in Emilio‘s opinion and experience tend to be quite modest and discreet. Thanks to referrals from friends in the banking community, over the years he has built a solid base of Argentine clients, and become friendly with many of them. (His Cuban-American family has become close with one particular group for whom he sold and managed units, and recently joined them to make some amazing wine in Mendoza, Argentina.)
But it would seem that the days of Argentines flying under Miami’s “real estate radar” are in the past. Some of the city’s most visible and exciting new projects are being created by developers with deep roots in Argentina, including:
- Mid-Miami Beach’s acclaimed Faena District, a six-block project that features luxury hotels, bars, condominiums, a cultural center and a retail complex, from the visionary mind of Argentine developer/artist Alan Faena.
- The Aston Martin Residences, the car maker’s first branded condominium project, which recently broke ground. The 66-story building located at the mouth of the Miami River is being developed by G&G Business Developments, a Miami-based firm owned by Argentine supermarket magnate German Coto and his mother Gloria.
- The Oceana-branded condominiums in Key Biscayne and Bal Harbour, created by Buenos Aires native (and international art collector) Eduardo Costantini.
In addition to these high-profile projects, observers may have noticed a quiet explosion of Argentine restaurants and other businesses in Miami over the past few years, reflecting the growing population of residents and visitors. From what Emilio has noticed, many of the wealthiest Argentines make their homes in Key Biscayne, but there are also many to be found in Aventura, Miami Beach, Brickell, Downtown, Midtown and Edgewater.
Unfortunately, not all news involving Argentine interest in Miami real estate have been positive.
Last month, The Miami Herald reported that former president Cristina Fernández de Kirchner was accused by the nation’s top anti-corruption official of secretly owning more than 60 Miami properties bought with “dirty money.”
While this item is concerning, Emilio believes that Argentina’s recent change in government, and the stability being demonstrated by its new reform-minded leadership, will put the country on a path toward sustained economic growth. This would obviously allow even more Argentine investment in Miami — the “clean” kind we very much prefer.
Emilio is looking forward to many more years of welcoming Argentines and others who continue to make Miami a dynamic, evolving, and truly international city.
Source: Miami Herald
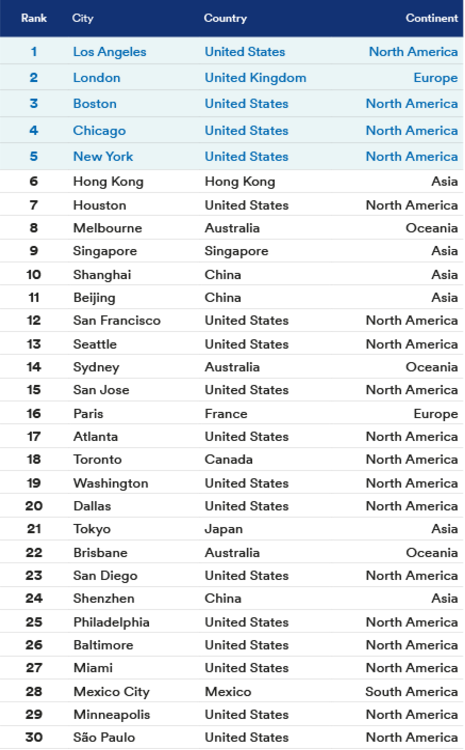
Miami was ranked by Schroders Global Cities Index for being a prime global location for real estate investment.
Coming in at no. 27, Miami is one of 18 American cities listed in the top 30 by Schroders.
The index utilized a number of factors to identify the most “economically vibrant cities” including the population age 15 and over as a way to gauge demand for goods and services, median household income, retail sales and gross domestic product. The index also factors potential future growth into its calculations and local university rankings.
“We see universities as being critical in powering city economies,” Tom Walker, the co-head of global real estate securities at Schroders, said. “Knowledge-based hubs are growing in economic strength with a positive knock-on to real estate markets in those locations.”
According to Forbes, the index is used by “wealthy, global real estate investors and by institutional firms looking for the best long term value for fixed asset investments.” Shroders is a top international asset management firm.
Out of those categories, Miami ranked highest in retail sales, with a rank of 12. Miami ranked 19th in population, 19th in median household income, 27th in university ranking and 22nd in gross domestic product output.
Miami is already known as a top spot for international property investors, and it’s inclusion on this list won’t hurt that distinction. And while Miami draws inordinately from South American buyers, perhaps inclusion on this list will help draw interest from European investors.
See the rankings of the top 30 cities below.
Source: Miami Agent Magazine
Many Miami real estate investors are doing their part to ward off global warming and save energy as the city ranked high for green commercial real estate.
A new study by CBRE Group and Maastrict University ranked Miami ninth in the nation, with 19.4 percent of its commercial real estate certified as green. There are 79 buildings totaling 21 million square feet of office space with either U.S. Green Building Council LEED certification or Energy Star labels.
Given that South Florida would be among the first places in the nation to be swamped by sea level rise, that’s a helpful move.
“Miami was slow to embrace green building standards relative to cities like San Francisco and Manhattan, but has caught up quickly thanks in part to good public policy and buy-in from owners and investors who realize there is growing demand from tenants for more sustainable, energy efficient space,” said Patricia Nooney, LEED AP, who leads investor services for CBRE Florida, in a news release.
In fact, Miami’s municipal code requires all new private development over 50,000 square feet to achieve LEED Silver certification.
The study rated Minneapolis as the greenest city for commercial real estate, with 77 percent of buildings certified as green.
Since 2005, the number of LEED certified buildings has increased more than 1,000 percent nationwide.
Florida homeowners are also going green. A recent study by the USGCB ranked Florida seventh for the most LEED-certified homes, with 1,860. California was first, with 9,186.
Source: SFBJ
As a city sitting virtually at sea level, Miami has been called ground zero for the problems posed by climate change, a place where rising sea levels threaten its future existence.
The latest forecast of sea level rise from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, for example, predicts that by later this century, global sea levels will be two feet higher than they are today, quite possibly higher. Under that scenario, the nuisance flooding in Miami that periodically comes with high tides will be a daily affair, the storm surge impact of hurricanes will be amplified, and lower-lying areas of the city will be uninhabitable. That’s actually not the worst of it: Under higher sea levels, the Biscayne Aquifer—where southeast Florida draws its drinking water—will increasingly suffer from saltwater intrusion, a problem for which there is no foreseen solution other than the investment of billions of dollars in water treatment facilities.
As bleak as this future would seem to be, few with real skin in the game in Miami—residents, real estate investors, and companies—are backing away from long-term investment. Exhibit A: Miami has been undergoing a nearly unprecedented surge in real estate construction, with planning discussions centering less on who will leave first and more on how high new projects can be built. Among the projects under way, for example, is an 80-plus-story behemoth in Brickell Center, the city’s urban core. If Miami is on the verge of being a modern-day Atlantis, those who would have the most to lose are apparently not buying it.
Why this apparent deafness to the dire warnings? Well, here’s a paradox. If one talks to developers and city commissioners in the area, it’s hard to find evidence of overt denial of current and future risk; Miami was a city, after all, almost completely destroyed by a hurricane in 1926, and most concede that a recurrence is a matter of when, not whether. Likewise, few deny that the city’s unique geography makes it vulnerable to the effects of rising sea levels. It’s a long-term problem that the planning commissions of Miami and Miami Beach acknowledge exists and threatens to get worse.
Where locals disagree with outsiders, however, is about how best to deal with the problem. Rather than sounding alarms and cutting back on development, there’s an implicit sense that the best approach may be, ironically, to do the opposite. And while a strong case can be made that this behavior has no rational basis, it may represent Miami’s best long-term hope for dealing with the threats posed by climate change, one that other cities might be advised to mimic: The best strategy, in fact, may be to foster a collective belief that there’s no threat—or at least not one serious enough to lose sleep over.
Before an explanation why, let’s first address the two standard explanations for the building boom, explanations that are indeed part of the puzzle. The first is that real estate developers, by their nature, are gamblers with short planning horizons. In the late 2000s, the real estate and equities crash quickly wiped out many builders. One might assume that would have made them skittish. To the contrary, the quick recovery that followed taught most that big risks are worth taking, and are survivable. While developers today may concede that sea levels are rising, it’s a risk that lies well beyond their investment horizons, and in any case is dwarfed by the more immediate risk of a returning recession.
The second explanation is that many of the buyers for all the new condo units are cash investors from Latin America, and the risks of Miami real estate—overdevelopment, speculation, environmental unsustainability—remain small relative to similar investments back home. No one is saying that real estate isn’t risky in Miami, or that sea level rise is fiction. What they are saying is that all investment carries risk, and development there is a bet they’re prepared to take.
But there’s another rational reason why even risk-averse residents in South Florida might, paradoxically, hope that buyers and sellers remain collectively naïve, or at least act as if they are, about the risks of sea level rise. South Florida relies almost exclusively on real estate taxes to fund public infrastructure. If the threat (or reality) of sea level rise suppresses property valuations, there will be less public money to address the risk. As an illustration, the head of public works for Miami Beach recently argued that the city would be wise to accelerate its investments in storm water drainage improvements ($100 million now and $400 million planned) simply because the city has the tax base to afford it—something it could not necessarily count on in the future.
Because buyers and sellers in Miami Beach have yet to connect the dots between nuisance flood events and the future consequences of sea level rise, property buyers continue to be drawn to the area, and development projects continue unabated—both of which are essential for a continued healthy tax base. If and when buyers and sellers do connect the dots, everything changes: Doing so could spark a rapid downward wealth spiral that, once initiated, would be difficult to reverse. Lowering property valuations would reduce the city’s tax revenue which, in turn, would leave it with less money to shore up the city against sea level rise. The city would then be forced to choose between two losing remedies: increase taxes on those who choose to stay, or decline to make the needed improvements. Both, of course, would only exacerbate the problem. Miami’s best move at that point would be to go hat in hand to the state and federal government for a bailout, but that seems unlikely. Quite aside from the “I-told-you-so” reactions that such pleas might evoke, almost all coastal communities would be facing similar problems and asking for commensurate help. Miami Beach as we know it now could cease to exist long before the Atlantic reclaims Collins Avenue.
Given this, South Florida’s best shot at coping with the long-term environmental threat may be a strategy that no doubt seems perverse to environmentalists: aggressively foster a collective belief that sea level rise is not something we urgently need to worry about. South Florida is potentially facing a huge adaptation bill down the road, and paying for it will require a healthy tax base. Keeping that tax base flush depends on a cooperative equilibrium where buyers and sellers maintain an optimistic view that it’s tomorrow’s problem, one that will be easily tackled when the time comes. This keeps the coffers filled and provides the resources needed to pay for the engineering adaptations required to keep the game going.
In this light, Miami’s construction cranes aren’t monuments to climate change denial. Quite to the contrary—they’re the instruments that may, indirectly, allow the city to survive global warming. Controlled ignorance, in some cases, can be a good thing.
Source: Bloomberg Businessweek
About Us
Ven-American Real Estate, Inc. established in 1991, is a full service commercial and residential real estate firm offering brokerage and property management services.
Subscribe
Contact Us
Ven-American Real Estate, Inc.
2401 SW 145th Avenue, Ste 407
Miramar, FL 33027
Brokerage & Property Management Services
Phone: 305-858-1188